1880-1900
| 1886
Arthur D. Little is founded by Dr. Arthur Dehon Little, a Massachusetts Institute of Technology Professor. The company emphasizes science, engineering and invention. Arthur D. Little still has an office within a stone's throw of the MIT campus. |
 |
 Alfred Marshall's Principles of Economics published. Introduces principles of partial equilibrium analysis (e.g. supply and demand curve plots) which shape the field of economics (and countless consulting projects) for a century. |
 |
1890
Frederick W. Taylor, a former engineer at the Midvale Steel Works, takes his emerging theory of Scientific Management and works as an active management consultant, performing studies of the time required to complete certain manufacturing tasks. This leads to wide use of time studies. |
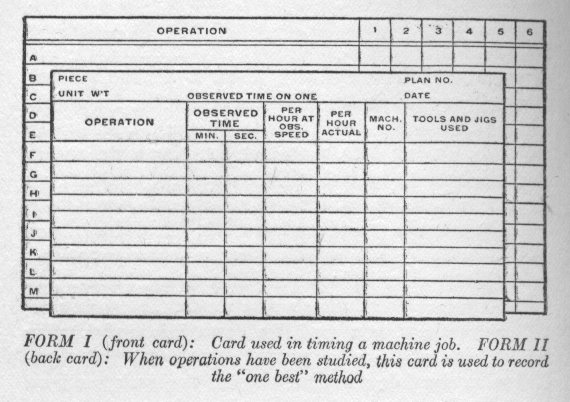 Form Used in an Early Time Study |
|
| 1898
The firm that later becomes Coopers & Lybrand and then PriceWaterhouseCoopers is founded with a focus on accounting practice. 1899 Harrington Emerson founds the Emerson Company, probably the first company managed like a generalist consulting firm of today. Most other early consulting firms had an engineering orientation in this period. |
EFFICIENCY means keen self-criticism. It means to go out into the shop and find nothing there that is sacred or fixed. It means that the shop six months ago shall be ancient history. It means the dropping of history, the forgetting of ghosts, the questioning of everything.
WILLIAM C. REDFIELD |